

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (9): 1252-1265.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.01252
• Special Issue on Prosocial Behavior (Part Ⅰ) • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Jing1, XU Boya1, YANG Ying2, ZHANG Qing-peng3, KOU Yu1( )
)
Published:2024-09-25
Online:2024-06-25
Contact:
KOU Yu, E-mail: LIN Jing, XU Boya, YANG Ying, ZHANG Qing-peng, KOU Yu. (2024). Network analysis and core dimensions of adolescent prosocial behavior. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(9), 1252-1265.
| Variable | Total sample | Primary school | Middle school | High school | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Boys | 4615 | 50.4 | 1771 | 51.3 | 1328 | 52.1 | 1516 | 48 |
| Girls | 4545 | 49.6 | 1681 | 48.7 | 1222 | 47.9 | 1642 | 52 |
| Father’s education level | ||||||||
| Junior high school and below | 2435 | 26.6 | 334 | 9.7 | 586 | 23 | 1515 | 48 |
| High school (including vocational high school and junior college) | 1853 | 20.2 | 669 | 19.4 | 492 | 19.3 | 692 | 21.9 |
| College | 897 | 9.8 | 408 | 11.8 | 200 | 7.8 | 289 | 9.2 |
| Undergraduate | 2209 | 24.1 | 1126 | 32.6 | 591 | 23.2 | 492 | 15.6 |
| Postgraduate and above | 1199 | 13.1 | 727 | 21.1 | 369 | 14.5 | 103 | 3.3 |
| Mother’s education level | ||||||||
| Junior high school and below | 2730 | 29.8 | 360 | 10.4 | 654 | 25.6 | 1716 | 54.3 |
| High school (including vocational high school and junior college) | 1793 | 19.6 | 746 | 21.6 | 430 | 16.9 | 617 | 19.5 |
| College | 1068 | 11.7 | 441 | 12.8 | 299 | 11.7 | 328 | 10.4 |
| Undergraduate | 2030 | 22.2 | 1074 | 31.1 | 586 | 23 | 370 | 11.7 |
| Postgraduate and above | 1005 | 11.0 | 659 | 19.1 | 281 | 11 | 65 | 2.1 |
| Monthly Family Income | ||||||||
| 2000 RMB and below | 680 | 7.4 | 165 | 4.8 | 49 | 1.9 | 466 | 14.8 |
| 2001~5000 RMB | 2317 | 25.3 | 839 | 24.3 | 469 | 18.4 | 1009 | 32 |
| 5001~10000 RMB | 2570 | 28.1 | 1031 | 29.9 | 705 | 27.6 | 834 | 26.4 |
| 10001~20000 RMB | 1772 | 19.3 | 688 | 19.9 | 578 | 22.7 | 506 | 16 |
| Above 20000RMB | 1213 | 13.2 | 544 | 15.8 | 421 | 16.5 | 248 | 7.9 |
Table 1 Demographic information
| Variable | Total sample | Primary school | Middle school | High school | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Boys | 4615 | 50.4 | 1771 | 51.3 | 1328 | 52.1 | 1516 | 48 |
| Girls | 4545 | 49.6 | 1681 | 48.7 | 1222 | 47.9 | 1642 | 52 |
| Father’s education level | ||||||||
| Junior high school and below | 2435 | 26.6 | 334 | 9.7 | 586 | 23 | 1515 | 48 |
| High school (including vocational high school and junior college) | 1853 | 20.2 | 669 | 19.4 | 492 | 19.3 | 692 | 21.9 |
| College | 897 | 9.8 | 408 | 11.8 | 200 | 7.8 | 289 | 9.2 |
| Undergraduate | 2209 | 24.1 | 1126 | 32.6 | 591 | 23.2 | 492 | 15.6 |
| Postgraduate and above | 1199 | 13.1 | 727 | 21.1 | 369 | 14.5 | 103 | 3.3 |
| Mother’s education level | ||||||||
| Junior high school and below | 2730 | 29.8 | 360 | 10.4 | 654 | 25.6 | 1716 | 54.3 |
| High school (including vocational high school and junior college) | 1793 | 19.6 | 746 | 21.6 | 430 | 16.9 | 617 | 19.5 |
| College | 1068 | 11.7 | 441 | 12.8 | 299 | 11.7 | 328 | 10.4 |
| Undergraduate | 2030 | 22.2 | 1074 | 31.1 | 586 | 23 | 370 | 11.7 |
| Postgraduate and above | 1005 | 11.0 | 659 | 19.1 | 281 | 11 | 65 | 2.1 |
| Monthly Family Income | ||||||||
| 2000 RMB and below | 680 | 7.4 | 165 | 4.8 | 49 | 1.9 | 466 | 14.8 |
| 2001~5000 RMB | 2317 | 25.3 | 839 | 24.3 | 469 | 18.4 | 1009 | 32 |
| 5001~10000 RMB | 2570 | 28.1 | 1031 | 29.9 | 705 | 27.6 | 834 | 26.4 |
| 10001~20000 RMB | 1772 | 19.3 | 688 | 19.9 | 578 | 22.7 | 506 | 16 |
| Above 20000RMB | 1213 | 13.2 | 544 | 15.8 | 421 | 16.5 | 248 | 7.9 |
| Abbreviation | Item | Dimension |
|---|---|---|
| PB01 | I like to participate in social welfare activities organised inside and outside the school. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB02 | I am willing to do things for the class collective. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB03 | I offer my seat to those who need it, such as the elderly, the sick, the disabled and the pregnant. | Altruism |
| PB04 | I will offer to invite bystanders to join our game. | Relationship |
| PB05 | I appreciate the hard work of my parents and take the initiative to do what I can around the house. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB06 | When a classmate is sick, I take the initiative to send him to the school clinic. | Altruism |
| PB07 | I will take the initiative to say hello to new students and make friends. | Relationship |
| PB08 | I am willing to correct my faults. | Traits |
| PB09 | When I am on duty, I spend more time cleaning the classroom. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB10 | I can keep others’ secrets. | Traits |
| PB11 | I will help my classmates with tutoring or teach them how to play ball. | Altruism |
| PB12 | When I have a small conflict with a friend, I apologise. | Relationship |
| PB13 | I greet teachers and elders when I meet them. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB14 | I often praise the virtues of others. | Traits |
| PB15 | I’d be happy to donate to the disaster area. | Altruism |
Table 2 Network nodes of prosocial behavior
| Abbreviation | Item | Dimension |
|---|---|---|
| PB01 | I like to participate in social welfare activities organised inside and outside the school. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB02 | I am willing to do things for the class collective. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB03 | I offer my seat to those who need it, such as the elderly, the sick, the disabled and the pregnant. | Altruism |
| PB04 | I will offer to invite bystanders to join our game. | Relationship |
| PB05 | I appreciate the hard work of my parents and take the initiative to do what I can around the house. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB06 | When a classmate is sick, I take the initiative to send him to the school clinic. | Altruism |
| PB07 | I will take the initiative to say hello to new students and make friends. | Relationship |
| PB08 | I am willing to correct my faults. | Traits |
| PB09 | When I am on duty, I spend more time cleaning the classroom. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB10 | I can keep others’ secrets. | Traits |
| PB11 | I will help my classmates with tutoring or teach them how to play ball. | Altruism |
| PB12 | When I have a small conflict with a friend, I apologise. | Relationship |
| PB13 | I greet teachers and elders when I meet them. | Commonweal-social rule |
| PB14 | I often praise the virtues of others. | Traits |
| PB15 | I’d be happy to donate to the disaster area. | Altruism |
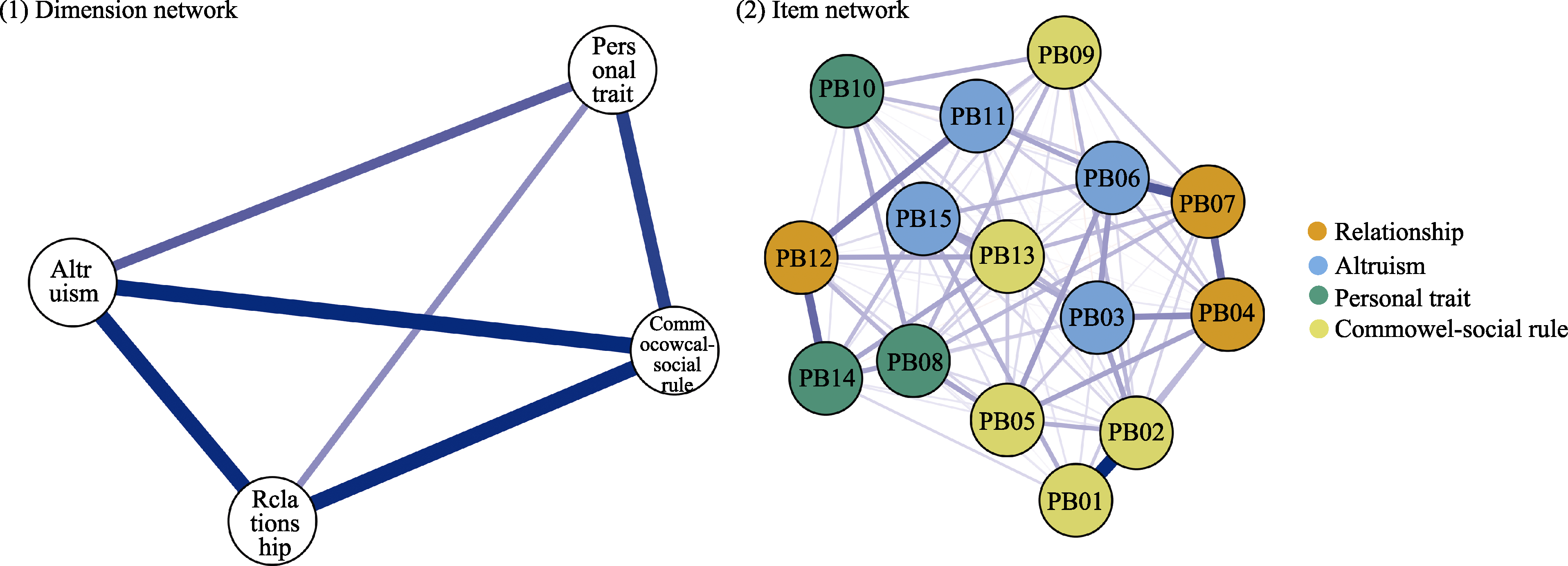
Figure 1. Total sample prosocial behavior dimensions and items networks. Note. Each node in the dimension network represents a prosocial behavior dimension, and each node in the topic network represents a prosocial behavior. The edge connecting two nodes represents the bias correlation between the two nodes, and the thickness of the edge indicates the strength of the bias correlation. The thicker the edge, the stronger the bias correlation, the thinner the edge, the weaker the bias correlation. Blue edges represent positive correlation; red edges represent negative correlation. Different prosocial behaviors within the same dimension are marked with the same colour (yellow = commonweal-social rule; orange = relationship; blue = altruism; green = trait). Specific descriptions corresponding to each node are shown in Table 2. The linkage values for all visualisation networks can be found in Supplementary Table 1 and 2.

Figure S1. Visualization of Dimensional Networks by Gender and Educational Stage, with the top left showing the network for primary school boys, top center for primary school girls, top right for middle school boys, bottom left for middle school girls, bottom center for high school boys, and bottom right for high school girls. Each node represents a dimension of prosocial behavior, and the edges between two nodes represent the partial correlation between them. The thickness of the edges indicates the strength of the partial correlation, with thicker edges indicating stronger correlations and thinner edges indicating weaker correlations. Blue edges denote positive correlations; red edges denote negative correlations.
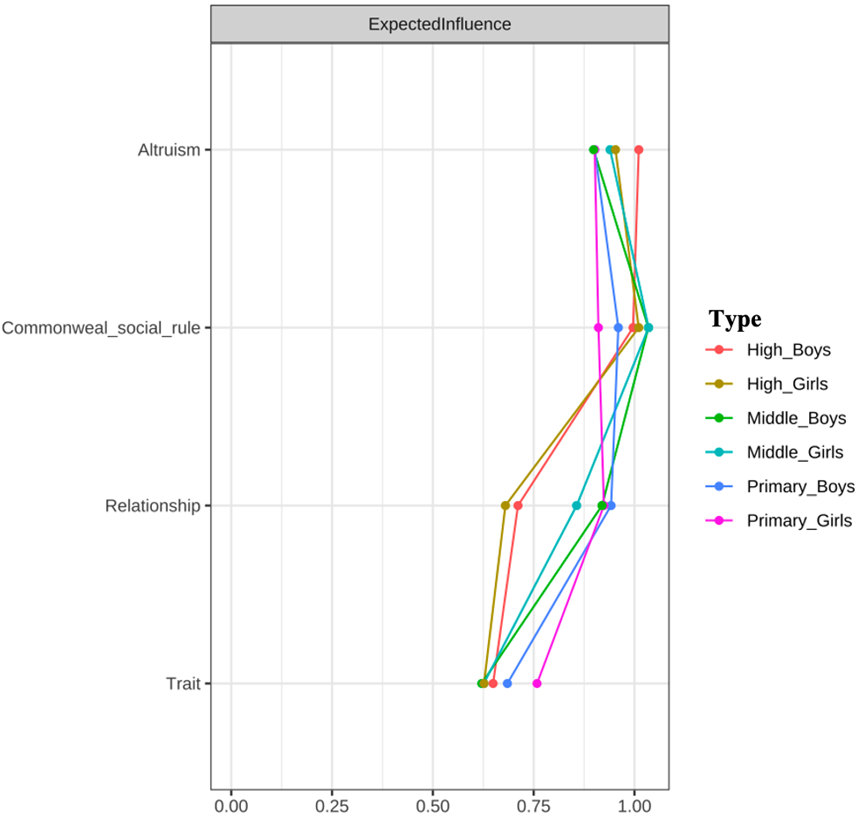
Figure S2. Centrality in Dimensional Networks by Gender and Educational Stage. The teal lines represent elementary school boys, green lines represent elementary school girls, yellow lines represent middle school boys, red lines represent middle school girls, magenta lines represent high school boys, and blue lines represent high school girls.
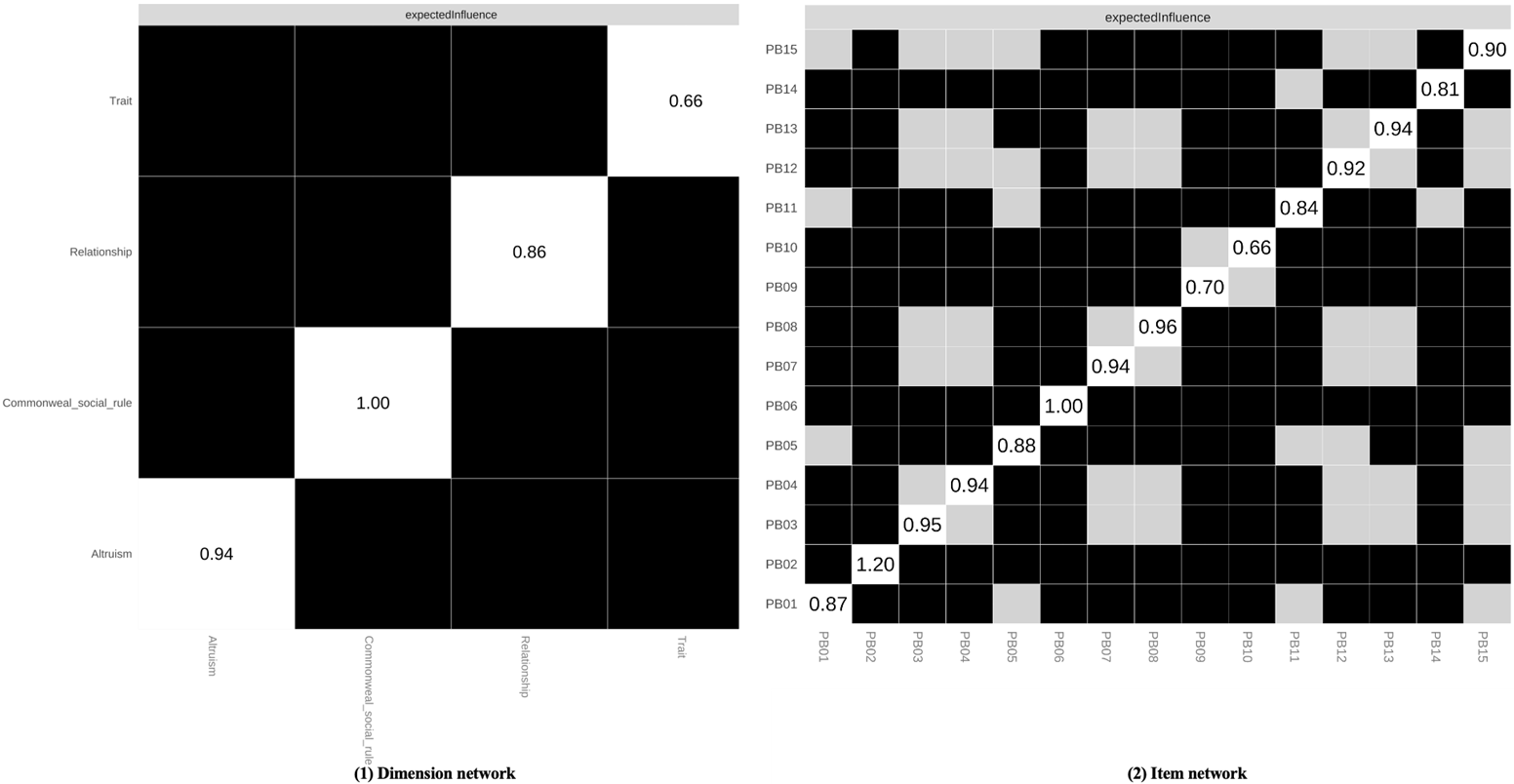
Figure S3. Test of Differences in Edge Strength between Overall Sample Dimensional Networks and Item Networks Note. A black box indicates a significant difference between two nodes, while a gray box indicates no significant difference between them.
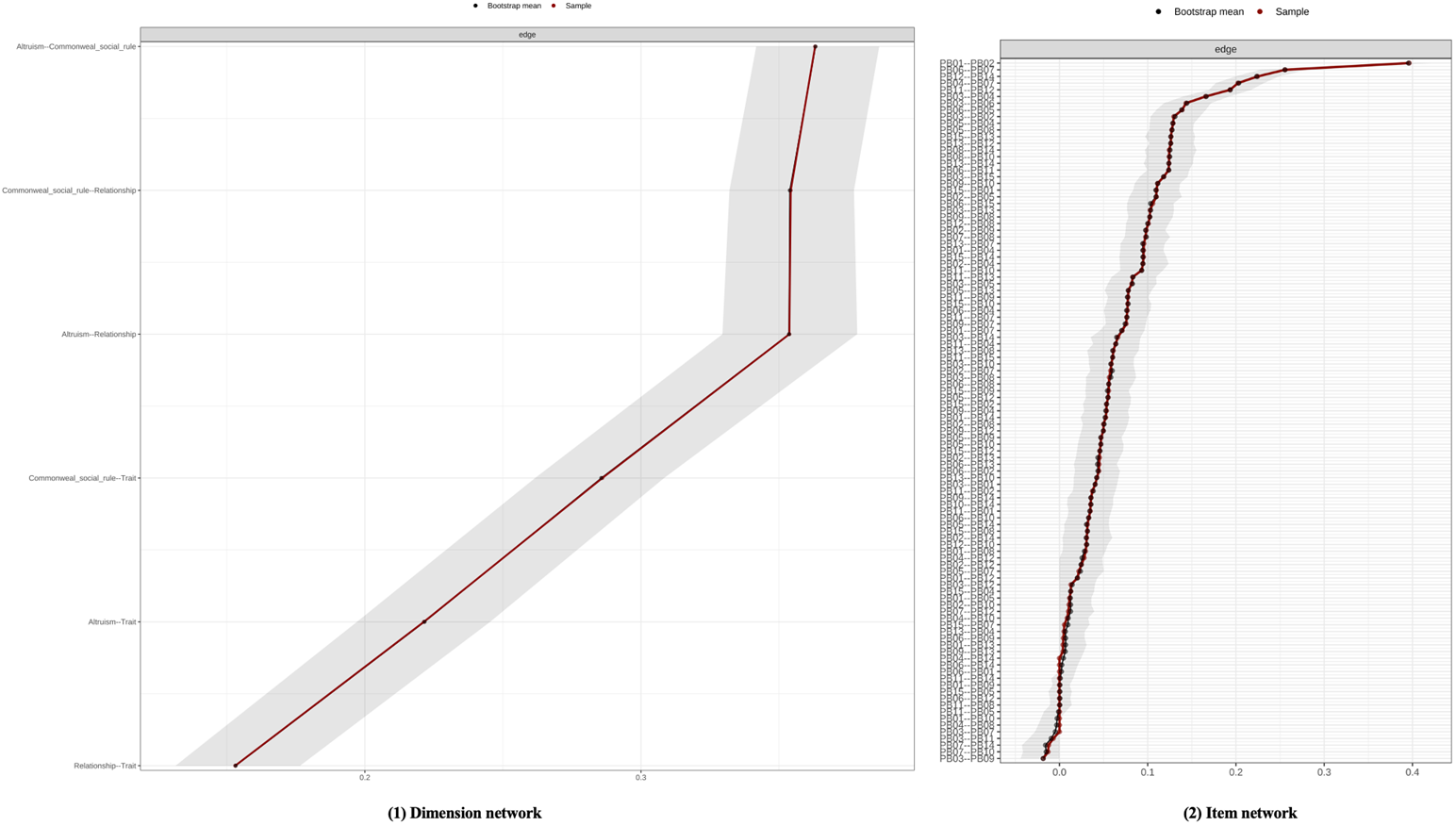
Figure S4. Bootstrap Confidence Intervals for Edge Weights in Overall Sample Dimensional Networks and Item Networks Note. The red line represents the edge weight value, and the gray area represents the 95% confidence interval.

Figure S6. Test of Differences in Edge Strength among Dimensional Networks by Educational Stage and Item Networks Note. A black box indicates a significant difference between two nodes, while a gray box indicates no significant difference between them.
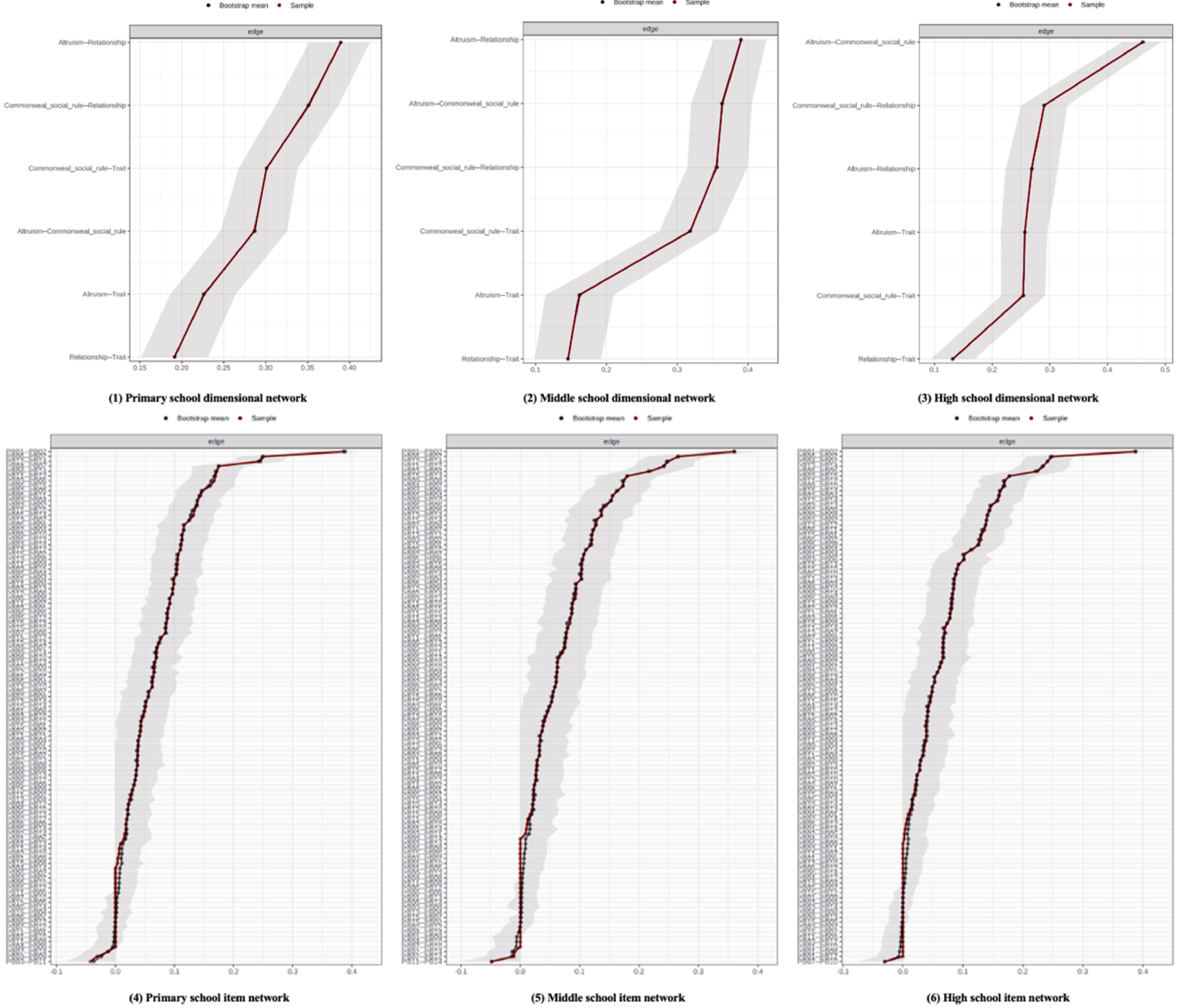
Figure S7. Bootstrap Confidence Intervals for Edge Weights in Dimensional Networks by Educational Stage and Item Networks Note. The red line represents the edge weight value, and the gray area represents the 95% confidence interval.
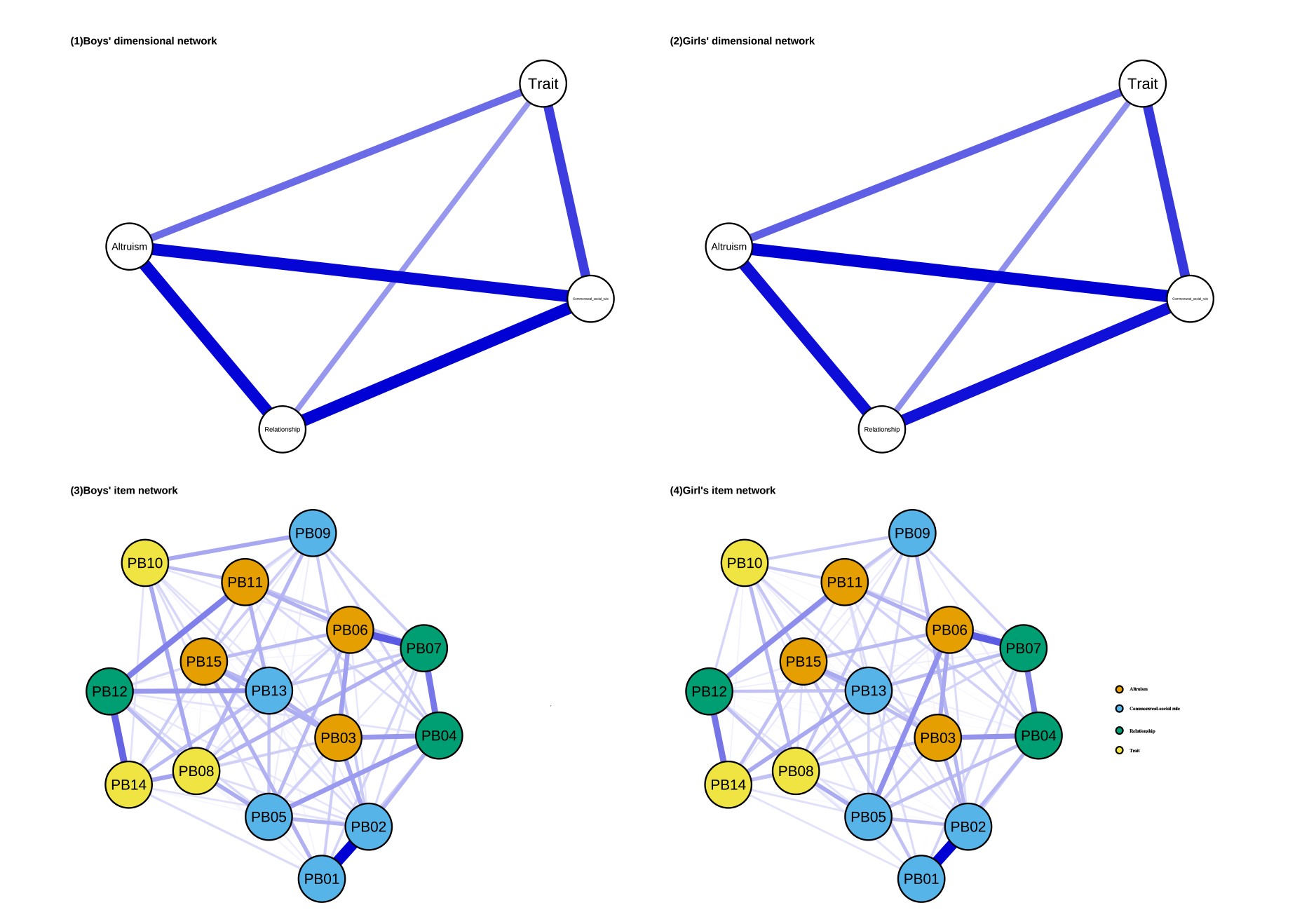
Figure S9. Visualization of Gender Dimensional Networks and Item Networks Note. Each node represents a dimension of prosocial behavior/item. The edges between two nodes indicate the partial correlation between them, with the thickness of the edges representing the strength of the partial correlation. Thicker edges indicate stronger correlations, while thinner edges indicate weaker correlations. Blue edges denote positive correlations, and red edges denote negative correlations.
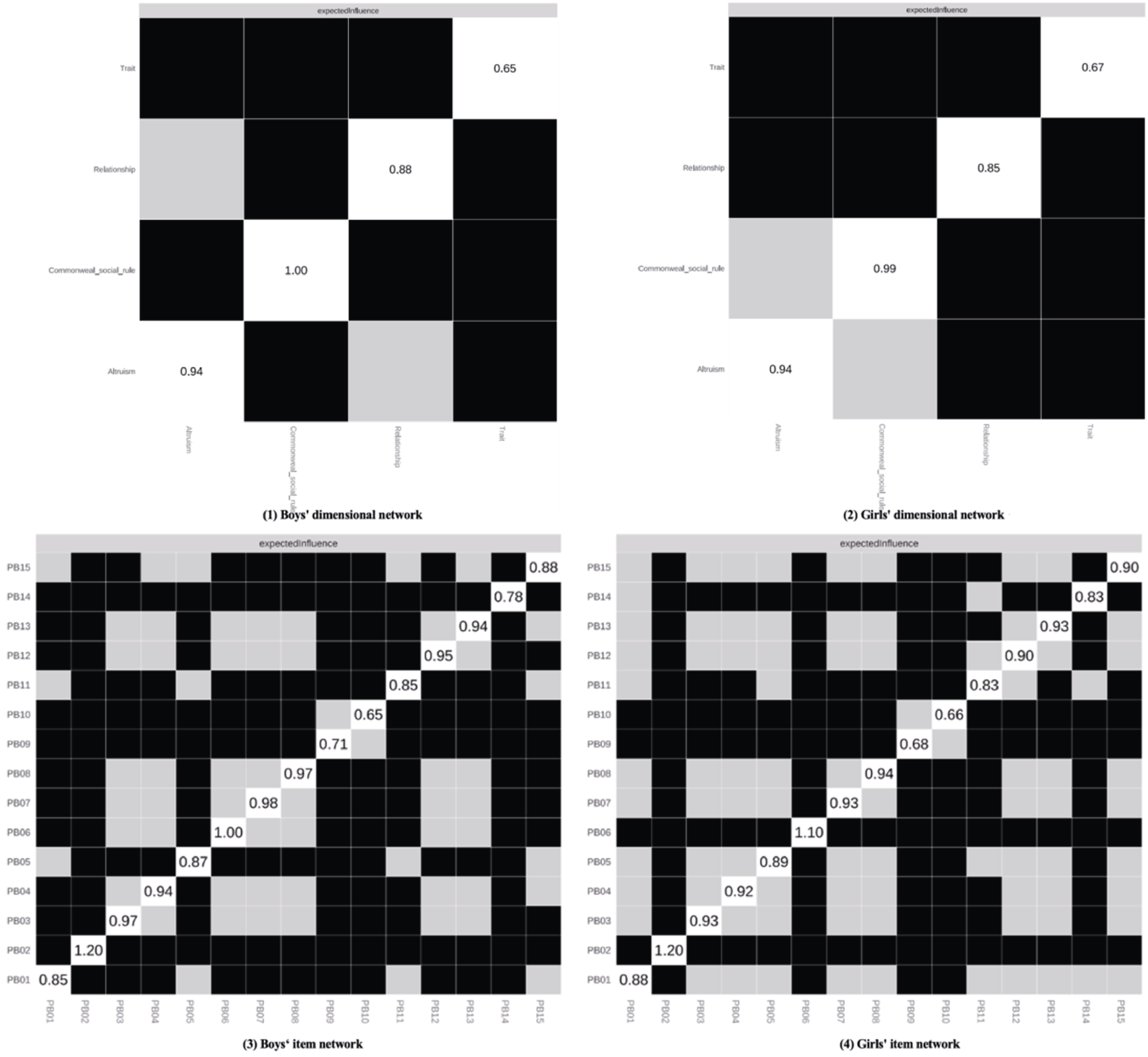
Figure S10. Test of Differences in Edge Strength between Gender Dimensional Networks and Item Networks Note. A black box indicates a significant difference between two nodes, while a gray box indicates no significant difference between them.

Figure S11. Bootstrap Confidence Intervals for Edge Weights in Gender Dimensional Networks and Item Networks Note. The red line represents the edge weight value, and the gray area represents the 95% confidence interval
| Dimensional Networks | Total sample | Boys | Girls | Primary | Middle | High | Boys vs. Girls (p value) | Primary vs. Middle (p value) | Middle vs. High (p value) | Primary vs. High (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonweal-social rule- Altruism | 0.363 | 0.36 | 0.364 | 0.286 | 0.364 | 0.462 | 0.866 | 0.005 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Relationship - Altruism | 0.354 | 0.362 | 0.345 | 0.39 | 0.391 | 0.269 | 0.463 | 0.967 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Traits - Altruism | 0.221 | 0.213 | 0.228 | 0.227 | 0.161 | 0.256 | 0.587 | 0.052 | 0.003 | 0.347 |
| Relationship-Commonweal-social rule | 0.354 | 0.367 | 0.341 | 0.352 | 0.355 | 0.29 | 0.254 | 0.902 | 0.032 | 0.023 |
| Traits-Commonweal-social rule | 0.286 | 0.282 | 0.286 | 0.301 | 0.319 | 0.254 | 0.871 | 0.557 | 0.034 | 0.096 |
| Traits - Relationship | 0.153 | 0.15 | 0.161 | 0.191 | 0.146 | 0.132 | 0.668 | 0.143 | 0.662 | 0.041 |
Table S1. Line Values and Test of Differences in Six Dimensional Networks
| Dimensional Networks | Total sample | Boys | Girls | Primary | Middle | High | Boys vs. Girls (p value) | Primary vs. Middle (p value) | Middle vs. High (p value) | Primary vs. High (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonweal-social rule- Altruism | 0.363 | 0.36 | 0.364 | 0.286 | 0.364 | 0.462 | 0.866 | 0.005 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Relationship - Altruism | 0.354 | 0.362 | 0.345 | 0.39 | 0.391 | 0.269 | 0.463 | 0.967 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Traits - Altruism | 0.221 | 0.213 | 0.228 | 0.227 | 0.161 | 0.256 | 0.587 | 0.052 | 0.003 | 0.347 |
| Relationship-Commonweal-social rule | 0.354 | 0.367 | 0.341 | 0.352 | 0.355 | 0.29 | 0.254 | 0.902 | 0.032 | 0.023 |
| Traits-Commonweal-social rule | 0.286 | 0.282 | 0.286 | 0.301 | 0.319 | 0.254 | 0.871 | 0.557 | 0.034 | 0.096 |
| Traits - Relationship | 0.153 | 0.15 | 0.161 | 0.191 | 0.146 | 0.132 | 0.668 | 0.143 | 0.662 | 0.041 |
| Item Networks | Total sample | Boys | Girls | Primary | Middle | High | Boys vs.Girls (p value) | Primary vs. Middle (p value) | Middle vs. High (p value) | Primary vs. High (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB01-PB02 | 0.396 | 0.378 | 0.409 | 0.389 | 0.361 | 0.388 | 0.191 | 0.379 | 0.380 | 0.986 |
| PB01-PB04 | 0.095 | 0.077 | 0.115 | 0.099 | 0.062 | 0.103 | 0.123 | 0.233 | 0.199 | 0.902 |
| PB01-PB05 | 0.011 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.172 | 0.650 | 1 | 0.627 |
| PB01-PB07 | 0.071 | 0.065 | 0.074 | 0.064 | 0.037 | 0.061 | 0.713 | 0.363 | 0.416 | 0.920 |
| PB01-PB08 | 0.030 | 0.017 | 0.046 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.000 | 0.237 | 0.781 | 0.008 | 0.075 |
| PB01-PB09 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.232 | 1 | 0.865 |
| PB01-PB10 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB01-PB12 | 0.020 | 0.016 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.756 | 0.065 | 0.006 | 1 |
| PB01-PB13 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.988 | 0.478 | 0.441 | 0.867 |
| PB01-PB14 | 0.052 | 0.055 | 0.047 | 0.132 | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.769 | < 0.001 | 0.863 | < 0.001 |
| PB02-PB04 | 0.095 | 0.112 | 0.074 | 0.115 | 0.103 | 0.053 | 0.152 | 0.708 | 0.131 | 0.048 |
| PB02-PB05 | 0.110 | 0.111 | 0.105 | 0.148 | 0.137 | 0.003 | 0.812 | 0.786 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| PB02-PB07 | 0.058 | 0.055 | 0.062 | 0.043 | 0.107 | 0.021 | 0.785 | 0.047 | 0.015 | 0.485 |
| PB02-PB08 | 0.050 | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.056 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.972 | 0.481 | 0.934 | 0.412 |
| PB02-PB09 | 0.098 | 0.078 | 0.118 | 0.066 | 0.103 | 0.145 | 0.085 | 0.175 | 0.173 | 0.002 |
| PB02-PB10 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.915 | 0.835 | 0.697 | 0.443 |
| PB02-PB12 | 0.025 | 0.037 | 0.012 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.041 | 0.323 | 0.259 | 0.125 | 0.409 |
| PB02-PB13 | 0.045 | 0.044 | 0.046 | 0.037 | 0.061 | 0.028 | 0.963 | 0.472 | 0.318 | 0.780 |
| PB02-PB14 | 0.031 | 0.043 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.093 | 0.007 | 0.271 | 0.029 | 0.013 | 0.555 |
| PB03-PB01 | 0.040 | 0.074 | 0.003 | 0.039 | 0.050 | 0.049 | 0.006 | 0.739 | 0.985 | 0.703 |
| PB03-PB02 | 0.130 | 0.135 | 0.122 | 0.138 | 0.120 | 0.140 | 0.598 | 0.594 | 0.596 | 0.969 |
| PB03-PB04 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.173 | 0.139 | 0.218 | 0.161 | 0.461 | 0.013 | 0.059 | 0.497 |
| PB03-PB05 | 0.082 | 0.071 | 0.092 | 0.089 | 0.061 | 0.079 | 0.441 | 0.411 | 0.640 | 0.754 |
| PB03-PB06 | 0.143 | 0.142 | 0.140 | 0.167 | 0.164 | 0.102 | 0.951 | 0.930 | 0.073 | 0.068 |
| PB03-PB07 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB03-PB08 | 0.056 | 0.069 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.084 | 0.039 | 0.378 | 0.176 | 0.189 | 0.949 |
| PB03-PB09 | -0.018 | 0.000 | -0.018 | -0.031 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.500 | 0.136 | 1 | 0.305 |
| PB03-PB10 | 0.059 | 0.042 | 0.074 | 0.048 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.243 | 0.633 | 0.898 | 0.734 |
| PB03-PB11 | -0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.043 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.479 | 0.048 |
| PB03-PB12 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.044 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.966 | 0.763 | 0.021 | 0.007 |
| PB03-PB13 | 0.103 | 0.117 | 0.083 | 0.097 | 0.092 | 0.147 | 0.186 | 0.869 | 0.102 | 0.115 |
| PB03-PB14 | 0.066 | 0.035 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.039 | < 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 |
| PB03-PB15 | 0.118 | 0.121 | 0.109 | 0.104 | 0.103 | 0.177 | 0.660 | 0.992 | 0.035 | 0.028 |
| PB04-PB07 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.200 | 0.175 | 0.173 | 0.241 | 0.946 | 0.953 | 0.041 | 0.036 |
| PB04-PB08 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB04-PB10 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.038 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.602 | 0.089 | 0.146 | 0.223 |
| PB04-PB12 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.008 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.150 | 0.919 | 0.406 | 0.456 |
| PB04-PB14 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.501 | 1 | 0.004 | 0.023 |
| PB05-PB04 | 0.129 | 0.149 | 0.105 | 0.103 | 0.156 | 0.115 | 0.092 | 0.109 | 0.196 | 0.704 |
| PB05-PB07 | 0.022 | 0.039 | 0.001 | 0.057 | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.185 | 0.332 | 0.072 | 0.057 |
| PB05-PB08 | 0.127 | 0.123 | 0.135 | 0.116 | 0.106 | 0.125 | 0.641 | 0.756 | 0.52 | 0.765 |
| PB05-PB09 | 0.047 | 0.028 | 0.067 | 0.032 | 0.047 | 0.083 | 0.117 | 0.598 | 0.267 | 0.059 |
| PB05-PB10 | 0.047 | 0.052 | 0.042 | 0.021 | 0.027 | 0.089 | 0.708 | 0.851 | 0.044 | 0.033 |
| PB05-PB12 | 0.055 | 0.057 | 0.048 | 0.088 | 0.033 | 0.005 | 0.716 | 0.08 | 0.396 | 0.010 |
| PB05-PB13 | 0.078 | 0.088 | 0.067 | 0.113 | 0.075 | 0.040 | 0.451 | 0.292 | 0.262 | 0.028 |
| PB05-PB14 | 0.032 | 0.013 | 0.050 | 0.018 | 0.065 | 0.016 | 0.173 | 0.152 | 0.160 | 0.930 |
| PB06-PB01 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.022 | 0.009 | 0.481 | 0.059 | 0.698 | 0.135 |
| PB06-PB02 | 0.045 | 0.036 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.038 | 0.130 | 0.450 | 0.148 | 0.005 | < 0.001 |
| PB06-PB04 | 0.077 | 0.076 | 0.080 | 0.063 | 0.094 | 0.086 | 0.906 | 0.392 | 0.823 | 0.476 |
| PB06-PB05 | 0.139 | 0.105 | 0.176 | 0.088 | 0.144 | 0.224 | 0.011 | 0.095 | 0.028 | < 0.001 |
| PB06-PB07 | 0.256 | 0.244 | 0.261 | 0.250 | 0.266 | 0.249 | 0.537 | 0.626 | 0.593 | 0.951 |
| PB06-PB08 | 0.056 | 0.071 | 0.036 | 0.092 | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.19 | 0.003 | 0.025 | 0.443 |
| PB06-PB09 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.957 | 0.365 | 1 | 0.528 |
| PB06-PB10 | 0.033 | 0.039 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.062 | 0.047 | 0.360 | 0.014 | 0.615 | 0.043 |
| PB06-PB11 | 0.124 | 0.115 | 0.127 | 0.144 | 0.071 | 0.136 | 0.594 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.769 |
| PB06-PB12 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.048 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB06-PB13 | 0.045 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 0.021 | 0.076 | 0.053 | 0.716 | 0.089 | 0.480 | 0.295 |
| PB06-PB14 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.264 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB06-PB15 | 0.106 | 0.100 | 0.109 | 0.160 | 0.088 | 0.020 | 0.739 | 0.029 | 0.044 | < 0.001 |
| PB07-PB08 | 0.098 | 0.117 | 0.068 | 0.084 | 0.128 | 0.067 | 0.052 | 0.165 | 0.063 | 0.564 |
| PB07-PB10 | -0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.030 | 1 | 1 | 0.427 | 0.133 |
| PB07-PB12 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.000 | -0.011 | 0.082 | 0.232 | 0.188 | < 0.001 | 0.002 |
| PB07-PB14 | -0.012 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.012 | -0.010 | 0.035 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.013 | 0.011 |
| PB08-PB10 | 0.124 | 0.127 | 0.115 | 0.070 | 0.153 | 0.169 | 0.66 | 0.026 | 0.590 | 0.002 |
| PB08-PB14 | 0.124 | 0.137 | 0.099 | 0.172 | 0.103 | 0.083 | 0.202 | 0.056 | 0.629 | 0.006 |
| PB09-PB04 | 0.053 | 0.069 | 0.036 | 0.039 | 0.080 | 0.036 | 0.181 | 0.185 | 0.132 | 0.921 |
| PB09-PB07 | 0.076 | 0.073 | 0.072 | 0.071 | 0.059 | 0.065 | 0.987 | 0.674 | 0.842 | 0.851 |
| PB09-PB08 | 0.102 | 0.110 | 0.093 | 0.035 | 0.174 | 0.141 | 0.489 | < 0.001 | 0.293 | < 0.001 |
| PB09-PB10 | 0.111 | 0.129 | 0.087 | 0.113 | 0.111 | 0.085 | 0.078 | 0.947 | 0.378 | 0.342 |
| PB09-PB12 | 0.050 | 0.039 | 0.059 | 0.033 | 0.078 | 0.040 | 0.407 | 0.144 | 0.220 | 0.810 |
| PB09-PB13 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.035 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.873 | 0.156 | 1 | 0.073 |
| PB09-PB14 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.070 | 0.000 | 0.040 | 0.950 | 0.015 | 0.084 | 0.323 |
| PB10-PB14 | 0.035 | 0.042 | 0.021 | 0.051 | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.428 | 0.349 | 0.848 | 0.252 |
| PB11-PB01 | 0.035 | 0.016 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.077 | 0.079 | 0.096 | < 0.001 | 0.953 | < 0.001 |
| PB11-PB02 | 0.037 | 0.029 | 0.048 | 0.027 | 0.024 | 0.067 | 0.446 | 0.911 | 0.152 | 0.160 |
| PB11-PB04 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.072 | 0.105 | 0.029 | 0.039 | 0.570 | 0.023 | 0.72 | 0.033 |
| PB11-PB05 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.169 | 0.182 | 0.063 | 1 |
| PB11-PB07 | 0.076 | 0.086 | 0.056 | 0.092 | 0.123 | 0.000 | 0.237 | 0.318 | < 0.001 | 0.002 |
| PB11-PB08 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.286 | 1 | 0.170 | 0.009 |
| PB11-PB09 | 0.078 | 0.064 | 0.090 | 0.099 | 0.026 | 0.067 | 0.288 | 0.020 | 0.211 | 0.298 |
| PB11-PB10 | 0.093 | 0.097 | 0.088 | 0.133 | 0.088 | 0.028 | 0.721 | 0.140 | 0.045 | < 0.001 |
| PB11-PB12 | 0.193 | 0.188 | 0.184 | 0.169 | 0.242 | 0.169 | 0.876 | 0.021 | 0.020 | 0.995 |
| PB11-PB13 | 0.083 | 0.114 | 0.053 | 0.067 | 0.084 | 0.086 | 0.011 | 0.583 | 0.949 | 0.535 |
| PB11-PB14 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.006 | -0.049 | 0.070 | 0.132 | 0.003 | < 0.001 | 0.005 |
| PB11-PB15 | 0.060 | 0.070 | 0.059 | 0.041 | 0.087 | 0.046 | 0.647 | 0.147 | 0.212 | 0.871 |
| PB12-PB08 | 0.101 | 0.101 | 0.104 | 0.096 | 0.094 | 0.082 | 0.917 | 0.933 | 0.728 | 0.660 |
| PB12-PB10 | 0.031 | 0.000 | 0.066 | 0.065 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.183 | 0.431 | 0.031 |
| PB12-PB14 | 0.225 | 0.230 | 0.221 | 0.245 | 0.249 | 0.158 | 0.736 | 0.902 | 0.012 | 0.005 |
| PB13-PB04 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.666 | 0.315 | 1 | 0.388 |
| PB13-PB07 | 0.096 | 0.083 | 0.107 | 0.125 | 0.033 | 0.069 | 0.316 | 0.005 | 0.197 | 0.067 |
| PB13-PB08 | 0.061 | 0.030 | 0.099 | 0.105 | 0.033 | 0.048 | 0.010 | 0.045 | 0.645 | 0.077 |
| PB13-PB10 | 0.042 | 0.048 | 0.033 | 0.062 | 0.043 | 0.023 | 0.582 | 0.552 | 0.525 | 0.163 |
| PB13-PB12 | 0.126 | 0.154 | 0.097 | 0.110 | 0.120 | 0.138 | 0.031 | 0.746 | 0.543 | 0.367 |
| PB13-PB14 | 0.124 | 0.102 | 0.138 | 0.051 | 0.137 | 0.234 | 0.194 | 0.010 | 0.007 | < 0.001 |
| PB15-PB01 | 0.110 | 0.115 | 0.100 | 0.043 | 0.120 | 0.130 | 0.557 | 0.017 | 0.749 | 0.003 |
| PB15-PB02 | 0.053 | 0.059 | 0.048 | 0.106 | 0.000 | 0.041 | 0.691 | 0.002 | 0.086 | 0.045 |
| PB15-PB04 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.247 | 0.248 | 0.922 | 0.495 |
| PB15-PB05 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.185 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB15-PB07 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.038 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.439 | 0.110 | 1 | 0.163 |
| PB15-PB08 | 0.032 | 0.015 | 0.050 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.067 | 0.219 | 0.684 | 0.155 | 0.050 |
| PB15-PB09 | 0.056 | 0.076 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.055 | 0.074 | 0.068 | 0.352 | 0.548 | 0.114 |
| PB15-PB10 | 0.077 | 0.061 | 0.094 | 0.085 | 0.053 | 0.091 | 0.204 | 0.315 | 0.228 | 0.881 |
| PB15-PB12 | 0.046 | 0.059 | 0.037 | 0.077 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.367 | 0.143 | 0.255 | 0.010 |
| PB15-PB13 | 0.126 | 0.107 | 0.137 | 0.086 | 0.180 | 0.093 | 0.279 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.812 |
| PB15-PB14 | 0.095 | 0.078 | 0.102 | 0.075 | 0.128 | 0.163 | 0.381 | 0.105 | 0.316 | 0.007 |
Table S2. Line Values and Test of Differences in Six Item Networks
| Item Networks | Total sample | Boys | Girls | Primary | Middle | High | Boys vs.Girls (p value) | Primary vs. Middle (p value) | Middle vs. High (p value) | Primary vs. High (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB01-PB02 | 0.396 | 0.378 | 0.409 | 0.389 | 0.361 | 0.388 | 0.191 | 0.379 | 0.380 | 0.986 |
| PB01-PB04 | 0.095 | 0.077 | 0.115 | 0.099 | 0.062 | 0.103 | 0.123 | 0.233 | 0.199 | 0.902 |
| PB01-PB05 | 0.011 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.172 | 0.650 | 1 | 0.627 |
| PB01-PB07 | 0.071 | 0.065 | 0.074 | 0.064 | 0.037 | 0.061 | 0.713 | 0.363 | 0.416 | 0.920 |
| PB01-PB08 | 0.030 | 0.017 | 0.046 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.000 | 0.237 | 0.781 | 0.008 | 0.075 |
| PB01-PB09 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.232 | 1 | 0.865 |
| PB01-PB10 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB01-PB12 | 0.020 | 0.016 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.756 | 0.065 | 0.006 | 1 |
| PB01-PB13 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.988 | 0.478 | 0.441 | 0.867 |
| PB01-PB14 | 0.052 | 0.055 | 0.047 | 0.132 | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.769 | < 0.001 | 0.863 | < 0.001 |
| PB02-PB04 | 0.095 | 0.112 | 0.074 | 0.115 | 0.103 | 0.053 | 0.152 | 0.708 | 0.131 | 0.048 |
| PB02-PB05 | 0.110 | 0.111 | 0.105 | 0.148 | 0.137 | 0.003 | 0.812 | 0.786 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| PB02-PB07 | 0.058 | 0.055 | 0.062 | 0.043 | 0.107 | 0.021 | 0.785 | 0.047 | 0.015 | 0.485 |
| PB02-PB08 | 0.050 | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.056 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.972 | 0.481 | 0.934 | 0.412 |
| PB02-PB09 | 0.098 | 0.078 | 0.118 | 0.066 | 0.103 | 0.145 | 0.085 | 0.175 | 0.173 | 0.002 |
| PB02-PB10 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.915 | 0.835 | 0.697 | 0.443 |
| PB02-PB12 | 0.025 | 0.037 | 0.012 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.041 | 0.323 | 0.259 | 0.125 | 0.409 |
| PB02-PB13 | 0.045 | 0.044 | 0.046 | 0.037 | 0.061 | 0.028 | 0.963 | 0.472 | 0.318 | 0.780 |
| PB02-PB14 | 0.031 | 0.043 | 0.012 | 0.016 | 0.093 | 0.007 | 0.271 | 0.029 | 0.013 | 0.555 |
| PB03-PB01 | 0.040 | 0.074 | 0.003 | 0.039 | 0.050 | 0.049 | 0.006 | 0.739 | 0.985 | 0.703 |
| PB03-PB02 | 0.130 | 0.135 | 0.122 | 0.138 | 0.120 | 0.140 | 0.598 | 0.594 | 0.596 | 0.969 |
| PB03-PB04 | 0.166 | 0.154 | 0.173 | 0.139 | 0.218 | 0.161 | 0.461 | 0.013 | 0.059 | 0.497 |
| PB03-PB05 | 0.082 | 0.071 | 0.092 | 0.089 | 0.061 | 0.079 | 0.441 | 0.411 | 0.640 | 0.754 |
| PB03-PB06 | 0.143 | 0.142 | 0.140 | 0.167 | 0.164 | 0.102 | 0.951 | 0.930 | 0.073 | 0.068 |
| PB03-PB07 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB03-PB08 | 0.056 | 0.069 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.084 | 0.039 | 0.378 | 0.176 | 0.189 | 0.949 |
| PB03-PB09 | -0.018 | 0.000 | -0.018 | -0.031 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.500 | 0.136 | 1 | 0.305 |
| PB03-PB10 | 0.059 | 0.042 | 0.074 | 0.048 | 0.063 | 0.058 | 0.243 | 0.633 | 0.898 | 0.734 |
| PB03-PB11 | -0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.043 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.479 | 0.048 |
| PB03-PB12 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.044 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.966 | 0.763 | 0.021 | 0.007 |
| PB03-PB13 | 0.103 | 0.117 | 0.083 | 0.097 | 0.092 | 0.147 | 0.186 | 0.869 | 0.102 | 0.115 |
| PB03-PB14 | 0.066 | 0.035 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.039 | < 0.001 | 1 | 0.001 |
| PB03-PB15 | 0.118 | 0.121 | 0.109 | 0.104 | 0.103 | 0.177 | 0.660 | 0.992 | 0.035 | 0.028 |
| PB04-PB07 | 0.202 | 0.202 | 0.200 | 0.175 | 0.173 | 0.241 | 0.946 | 0.953 | 0.041 | 0.036 |
| PB04-PB08 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB04-PB10 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.038 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.602 | 0.089 | 0.146 | 0.223 |
| PB04-PB12 | 0.028 | 0.043 | 0.008 | 0.022 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.150 | 0.919 | 0.406 | 0.456 |
| PB04-PB14 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.043 | 0.501 | 1 | 0.004 | 0.023 |
| PB05-PB04 | 0.129 | 0.149 | 0.105 | 0.103 | 0.156 | 0.115 | 0.092 | 0.109 | 0.196 | 0.704 |
| PB05-PB07 | 0.022 | 0.039 | 0.001 | 0.057 | 0.021 | 0.000 | 0.185 | 0.332 | 0.072 | 0.057 |
| PB05-PB08 | 0.127 | 0.123 | 0.135 | 0.116 | 0.106 | 0.125 | 0.641 | 0.756 | 0.52 | 0.765 |
| PB05-PB09 | 0.047 | 0.028 | 0.067 | 0.032 | 0.047 | 0.083 | 0.117 | 0.598 | 0.267 | 0.059 |
| PB05-PB10 | 0.047 | 0.052 | 0.042 | 0.021 | 0.027 | 0.089 | 0.708 | 0.851 | 0.044 | 0.033 |
| PB05-PB12 | 0.055 | 0.057 | 0.048 | 0.088 | 0.033 | 0.005 | 0.716 | 0.08 | 0.396 | 0.010 |
| PB05-PB13 | 0.078 | 0.088 | 0.067 | 0.113 | 0.075 | 0.040 | 0.451 | 0.292 | 0.262 | 0.028 |
| PB05-PB14 | 0.032 | 0.013 | 0.050 | 0.018 | 0.065 | 0.016 | 0.173 | 0.152 | 0.160 | 0.930 |
| PB06-PB01 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.022 | 0.009 | 0.481 | 0.059 | 0.698 | 0.135 |
| PB06-PB02 | 0.045 | 0.036 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.038 | 0.130 | 0.450 | 0.148 | 0.005 | < 0.001 |
| PB06-PB04 | 0.077 | 0.076 | 0.080 | 0.063 | 0.094 | 0.086 | 0.906 | 0.392 | 0.823 | 0.476 |
| PB06-PB05 | 0.139 | 0.105 | 0.176 | 0.088 | 0.144 | 0.224 | 0.011 | 0.095 | 0.028 | < 0.001 |
| PB06-PB07 | 0.256 | 0.244 | 0.261 | 0.250 | 0.266 | 0.249 | 0.537 | 0.626 | 0.593 | 0.951 |
| PB06-PB08 | 0.056 | 0.071 | 0.036 | 0.092 | 0.000 | 0.067 | 0.19 | 0.003 | 0.025 | 0.443 |
| PB06-PB09 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.957 | 0.365 | 1 | 0.528 |
| PB06-PB10 | 0.033 | 0.039 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.062 | 0.047 | 0.360 | 0.014 | 0.615 | 0.043 |
| PB06-PB11 | 0.124 | 0.115 | 0.127 | 0.144 | 0.071 | 0.136 | 0.594 | 0.024 | 0.027 | 0.769 |
| PB06-PB12 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.048 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB06-PB13 | 0.045 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 0.021 | 0.076 | 0.053 | 0.716 | 0.089 | 0.480 | 0.295 |
| PB06-PB14 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.264 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB06-PB15 | 0.106 | 0.100 | 0.109 | 0.160 | 0.088 | 0.020 | 0.739 | 0.029 | 0.044 | < 0.001 |
| PB07-PB08 | 0.098 | 0.117 | 0.068 | 0.084 | 0.128 | 0.067 | 0.052 | 0.165 | 0.063 | 0.564 |
| PB07-PB10 | -0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.030 | 1 | 1 | 0.427 | 0.133 |
| PB07-PB12 | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.000 | -0.011 | 0.082 | 0.232 | 0.188 | < 0.001 | 0.002 |
| PB07-PB14 | -0.012 | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.012 | -0.010 | 0.035 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.013 | 0.011 |
| PB08-PB10 | 0.124 | 0.127 | 0.115 | 0.070 | 0.153 | 0.169 | 0.66 | 0.026 | 0.590 | 0.002 |
| PB08-PB14 | 0.124 | 0.137 | 0.099 | 0.172 | 0.103 | 0.083 | 0.202 | 0.056 | 0.629 | 0.006 |
| PB09-PB04 | 0.053 | 0.069 | 0.036 | 0.039 | 0.080 | 0.036 | 0.181 | 0.185 | 0.132 | 0.921 |
| PB09-PB07 | 0.076 | 0.073 | 0.072 | 0.071 | 0.059 | 0.065 | 0.987 | 0.674 | 0.842 | 0.851 |
| PB09-PB08 | 0.102 | 0.110 | 0.093 | 0.035 | 0.174 | 0.141 | 0.489 | < 0.001 | 0.293 | < 0.001 |
| PB09-PB10 | 0.111 | 0.129 | 0.087 | 0.113 | 0.111 | 0.085 | 0.078 | 0.947 | 0.378 | 0.342 |
| PB09-PB12 | 0.050 | 0.039 | 0.059 | 0.033 | 0.078 | 0.040 | 0.407 | 0.144 | 0.220 | 0.810 |
| PB09-PB13 | 0.004 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.035 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.873 | 0.156 | 1 | 0.073 |
| PB09-PB14 | 0.036 | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.070 | 0.000 | 0.040 | 0.950 | 0.015 | 0.084 | 0.323 |
| PB10-PB14 | 0.035 | 0.042 | 0.021 | 0.051 | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.428 | 0.349 | 0.848 | 0.252 |
| PB11-PB01 | 0.035 | 0.016 | 0.056 | 0.000 | 0.077 | 0.079 | 0.096 | < 0.001 | 0.953 | < 0.001 |
| PB11-PB02 | 0.037 | 0.029 | 0.048 | 0.027 | 0.024 | 0.067 | 0.446 | 0.911 | 0.152 | 0.160 |
| PB11-PB04 | 0.064 | 0.058 | 0.072 | 0.105 | 0.029 | 0.039 | 0.570 | 0.023 | 0.72 | 0.033 |
| PB11-PB05 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.169 | 0.182 | 0.063 | 1 |
| PB11-PB07 | 0.076 | 0.086 | 0.056 | 0.092 | 0.123 | 0.000 | 0.237 | 0.318 | < 0.001 | 0.002 |
| PB11-PB08 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.286 | 1 | 0.170 | 0.009 |
| PB11-PB09 | 0.078 | 0.064 | 0.090 | 0.099 | 0.026 | 0.067 | 0.288 | 0.020 | 0.211 | 0.298 |
| PB11-PB10 | 0.093 | 0.097 | 0.088 | 0.133 | 0.088 | 0.028 | 0.721 | 0.140 | 0.045 | < 0.001 |
| PB11-PB12 | 0.193 | 0.188 | 0.184 | 0.169 | 0.242 | 0.169 | 0.876 | 0.021 | 0.020 | 0.995 |
| PB11-PB13 | 0.083 | 0.114 | 0.053 | 0.067 | 0.084 | 0.086 | 0.011 | 0.583 | 0.949 | 0.535 |
| PB11-PB14 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.006 | -0.049 | 0.070 | 0.132 | 0.003 | < 0.001 | 0.005 |
| PB11-PB15 | 0.060 | 0.070 | 0.059 | 0.041 | 0.087 | 0.046 | 0.647 | 0.147 | 0.212 | 0.871 |
| PB12-PB08 | 0.101 | 0.101 | 0.104 | 0.096 | 0.094 | 0.082 | 0.917 | 0.933 | 0.728 | 0.660 |
| PB12-PB10 | 0.031 | 0.000 | 0.066 | 0.065 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.183 | 0.431 | 0.031 |
| PB12-PB14 | 0.225 | 0.230 | 0.221 | 0.245 | 0.249 | 0.158 | 0.736 | 0.902 | 0.012 | 0.005 |
| PB13-PB04 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.666 | 0.315 | 1 | 0.388 |
| PB13-PB07 | 0.096 | 0.083 | 0.107 | 0.125 | 0.033 | 0.069 | 0.316 | 0.005 | 0.197 | 0.067 |
| PB13-PB08 | 0.061 | 0.030 | 0.099 | 0.105 | 0.033 | 0.048 | 0.010 | 0.045 | 0.645 | 0.077 |
| PB13-PB10 | 0.042 | 0.048 | 0.033 | 0.062 | 0.043 | 0.023 | 0.582 | 0.552 | 0.525 | 0.163 |
| PB13-PB12 | 0.126 | 0.154 | 0.097 | 0.110 | 0.120 | 0.138 | 0.031 | 0.746 | 0.543 | 0.367 |
| PB13-PB14 | 0.124 | 0.102 | 0.138 | 0.051 | 0.137 | 0.234 | 0.194 | 0.010 | 0.007 | < 0.001 |
| PB15-PB01 | 0.110 | 0.115 | 0.100 | 0.043 | 0.120 | 0.130 | 0.557 | 0.017 | 0.749 | 0.003 |
| PB15-PB02 | 0.053 | 0.059 | 0.048 | 0.106 | 0.000 | 0.041 | 0.691 | 0.002 | 0.086 | 0.045 |
| PB15-PB04 | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.247 | 0.248 | 0.922 | 0.495 |
| PB15-PB05 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.185 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PB15-PB07 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.038 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.439 | 0.110 | 1 | 0.163 |
| PB15-PB08 | 0.032 | 0.015 | 0.050 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.067 | 0.219 | 0.684 | 0.155 | 0.050 |
| PB15-PB09 | 0.056 | 0.076 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.055 | 0.074 | 0.068 | 0.352 | 0.548 | 0.114 |
| PB15-PB10 | 0.077 | 0.061 | 0.094 | 0.085 | 0.053 | 0.091 | 0.204 | 0.315 | 0.228 | 0.881 |
| PB15-PB12 | 0.046 | 0.059 | 0.037 | 0.077 | 0.027 | 0.000 | 0.367 | 0.143 | 0.255 | 0.010 |
| PB15-PB13 | 0.126 | 0.107 | 0.137 | 0.086 | 0.180 | 0.093 | 0.279 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.812 |
| PB15-PB14 | 0.095 | 0.078 | 0.102 | 0.075 | 0.128 | 0.163 | 0.381 | 0.105 | 0.316 | 0.007 |
| Centrality | Boys vs. Girls (p value) | Primary vs. Middle (p value) | Middle vs. High (p value) | Primary vs. High (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | 0.325 | 0.863 | 0.985 | 0.901 |
| PB02 | 0.784 | 0.588 | 0.093 | 0.242 |
| PB03 | 0.213 | 0.142 | 0.298 | 0.774 |
| PB04 | 0.528 | 0.398 | 0.118 | 0.571 |
| PB05 | 0.581 | 0.952 | 0.012 | 0.007 |
| PB06 | 0.075 | 0.635 | 0.036 | < 0.001 |
| PB07 | 0.099 | 0.117 | 0.105 | < 0.001 |
| PB08 | 0.390 | 0.230 | 0.768 | 0.345 |
| PB09 | 0.347 | 0.003 | 0.297 | < 0.001 |
| PB10 | 0.713 | 0.308 | 0.159 | 0.006 |
| PB11 | 0.676 | 0.669 | 0.893 | 0.593 |
| PB12 | 0.104 | 0.936 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| PB13 | 0.710 | 0.850 | 0.388 | 0.432 |
| PB14 | 0.130 | < 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.047 |
| PB15 | 0.493 | 0.429 | 0.366 | 0.069 |
Table S3. Test of Differences in Centrality Indices for Gender and Educational Stage Item Networks
| Centrality | Boys vs. Girls (p value) | Primary vs. Middle (p value) | Middle vs. High (p value) | Primary vs. High (p value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | 0.325 | 0.863 | 0.985 | 0.901 |
| PB02 | 0.784 | 0.588 | 0.093 | 0.242 |
| PB03 | 0.213 | 0.142 | 0.298 | 0.774 |
| PB04 | 0.528 | 0.398 | 0.118 | 0.571 |
| PB05 | 0.581 | 0.952 | 0.012 | 0.007 |
| PB06 | 0.075 | 0.635 | 0.036 | < 0.001 |
| PB07 | 0.099 | 0.117 | 0.105 | < 0.001 |
| PB08 | 0.390 | 0.230 | 0.768 | 0.345 |
| PB09 | 0.347 | 0.003 | 0.297 | < 0.001 |
| PB10 | 0.713 | 0.308 | 0.159 | 0.006 |
| PB11 | 0.676 | 0.669 | 0.893 | 0.593 |
| PB12 | 0.104 | 0.936 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| PB13 | 0.710 | 0.850 | 0.388 | 0.432 |
| PB14 | 0.130 | < 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.047 |
| PB15 | 0.493 | 0.429 | 0.366 | 0.069 |
| [1] | Baber, M. A. (2016). Appropriate school starting age: A focus on the cognitive and social development of a child. Journal of Education and Educational Development, 3(2), 277-287. |
| [2] | Batson, C. D., van Lange, P. A. M., Ahmad, N., & Lishner, D. A. (2003). Altruism and helping behavior. In M. A. Hogg, & J. Cooper (Eds.), Sage handbook of social psychology (pp. 279-295). Sage. |
| [3] | Blakemore, S.-J., & Mills, K. L. (2014). Is adolescence a sensitive period for sociocultural processing? Annual Review of Psychology, 65, 187-207. |
| [4] | Blanchard, M. A., & Heeren, A. (2020). Why we should move from reductionism and embrace a network approach to parental burnout. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 2020(174), 159-168. |
| [5] | Boccaletti, S., Latora, V., Moreno, Y., Chavez, M., & Hwang, D.-U. (2006). Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Physics Reports, 424(4-5), 175-308. |
| [6] |
Borsboom, D., & Cramer, A. O. J. (2013). Network analysis: An integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9, 91-121.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185608 pmid: 23537483 |
| [7] |
Briganti, G., Kempenaers, C., Braun, S., Fried, E. I., & Linkowski, P. (2018). Network analysis of empathy items from the interpersonal reactivity index in 1973 young adults. Psychiatry Research, 265, 87-92.
doi: S0165-1781(17)31682-7 pmid: 29702306 |
| [8] | Caprara, G. V., Kanacri, B. P. L., Gerbino, M., Zuffianò, A., Alessandri, G., Vecchio, G., Caprara, E., Pastorelli, C., & Bridglall, B. (2014). Positive effects of promoting prosocial behavior in early adolescence. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 38(4), 386-396. |
| [9] | Carlo, G. (2013). The development and correlates of prosocial moral behavior. Handbook of moral development (2nd Ed.). Psychology Press. |
| [10] | Carlo, G., Mestre, M. V., McGinley, M. M., Tur‐Porcar, A., Samper, P., & Opal, D. (2014). The protective role of prosocial behavior on antisocial behavior: The mediating effects of deviant peer affiliation. Journal of Adolescence, 37(4), 359-366. |
| [11] | Carlo, G., & Padilla‐Walker, L. (2020). Adolescents’ prosocial behavior through a multidimensional and multicultural lens. Child Development Perspectives, 14(4), 265-272. |
| [12] | Carlo, G., Padilla-Walker, L. M., & Nielson, M. G. (2015). Longitudinal bidirectional relations between adolescents’ sympathy and prosocial behavior. Developmental Psychology, 51(12), 1771-1777. |
| [13] | Carlo, G., & Pierotti, S. L. (2020). The development of prosocial motives. In L. A. Jensen (Ed.), Oxford handbook of moral development: An interdisciplinary perspective (pp. 27-51). Oxford University Press. |
| [14] | Carlo, G., & Randall, B. A. (2002). The development of a measure of prosocial behavior for late adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 31(1), 31-44. |
| [15] | Chen, X., Liu, M., Rubin, K. H., Cen, G., Gao, X., & Li, D. (2002). Sociability and prosocial orientation as predictors of youth adjustment: A seven-year longitudinal study in a Chinese sample. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 26(2), 128-136. |
| [16] | Costantini, G., Epskamp, S., Borsboom, D., Perugini, M., Mõttus, R., Waldorp, L. J., & Cramer, A. O. J. (2015). State of the aRt personality research: A tutorial on network analysis of personality data in R. Journal of Research in Personality, 54, 13-29. |
| [17] | Costantini, G., Richetin, J., Borsboom, D., Fried, E. I., Rhemtulla, M., & Perugini, M. (2015). Development of indirect measures of conscientiousness: Combining a facets approach and network analysis. European Journal of Personality, 29(5), 548-567. |
| [18] | Cramer, A. O. J., Van Der Sluis, S., Noordhof, A., Wichers, M., Geschwind, N., Aggen, S. H., Kendler, K. S., & Borsboom, D. (2012). Dimensions of normal personality as networks in search of equilibrium: You can’t like parties if you don’t like people. European Journal of Personality, 26(4), 414-431. |
| [19] |
Dalege, J., Borsboom, D., van Harreveld, F., van den Berg, H., Conner, M., & van der Maas, H. L. J. (2016). Toward a formalized account of attitudes: The Causal Attitude Network (CAN) model. Psychological Review, 123(1), 2-22.
doi: 10.1037/a0039802 pmid: 26479706 |
| [20] |
Eagly, A. H. (2009). The his and hers of prosocial behavior: An examination of the social psychology of gender. American Psychologist, 64(8), 644-658.
doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.64.8.644 pmid: 19899859 |
| [21] | Eisenberg, N. (2000). Emotion, regulation, and moral development. Annual Review of Psychology, 51(1), 665-697. |
| [22] |
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., Guthrie, I. K., Murphy, B. C., & Shepard, S. A. (2005). Age changes in prosocial responding and moral reasoning in adolescence and early adulthood. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 15(3), 235-260.
doi: 10.1111/j.1532-7795.2005.00095.x pmid: 20592955 |
| [23] | Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., & Spinrad, T. L. (2006). Prosocial development. In N. Eisenberg, W. Damon, & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Social, emotional, and personality development (Vol. 3, 6th ed. pp. 646-718). John Wiley & Sons Inc. |
| [24] |
Epskamp, S., Borsboom, D., & Fried, E. I. (2018). Estimating psychological networks and their accuracy: A tutorial paper. Behavior Research Methods, 50(1), 195-212.
doi: 10.3758/s13428-017-0862-1 pmid: 28342071 |
| [25] |
Epskamp, S., & Fried, E. I. (2018). A tutorial on regularized partial correlation networks. Psychological Methods, 23(4), 617-634.
doi: 10.1037/met0000167 pmid: 29595293 |
| [26] | Fabes, R. A., Carlo, G., Kupanoff, K., & Laible, D. (1999). Early adolescence and prosocial/moral behavior I: The role of individual processes. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 19(1), 5-16. |
| [27] | Fagot, B. I., Rodgers, C. S., & Leinbach, M. D. (2000). Theories of gender socialization. In T. Eckes & H. M. Trautner (Eds.), The developmental social psychology of gender (pp. 65-89). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. |
| [28] | Fried, E. I., van Borkulo, C. D., Cramer, A. O. J., Boschloo, L., Schoevers, R. A., & Borsboom, D. (2017). Mental disorders as networks of problems: A review of recent insights. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology: The International Journal for Research in Social and Genetic Epidemiology and Mental Health Services, 52(1), 1-10. |
| [29] | Funkhouser, C. J., Chacko, A. A., Correa, K. A., Kaiser, A. J. E., & Shankman, S. A. (2021). Unique longitudinal relationships between symptoms of psychopathology in youth: A cross‐lagged panel network analysis in the ABCD study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 62(2), 184-194. |
| [30] | Goldstein, S. E., Boxer, P., & Rudolph, E. (2015). Middle school transition stress: Links with academic performance, motivation, and school experiences. Contemporary School Psychology, 19(1), 21-29. |
| [31] | Hart, D., & Carlo, G. (2005). Moral development in adolescence. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 15(3), 223-233. |
| [32] |
Hevey, D. (2018). Network analysis: A brief overview and tutorial. Health Psychology and Behavioral Medicine, 6(1), 301-328.
doi: 10.1080/21642850.2018.1521283 pmid: 34040834 |
| [33] | Kou, Y., & Lei, Wang.. (2003). Review of research on children’s prosocial behavior and its interventions. Psychological Development and Education, (4), 86-91. |
| [34] | Kou, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2006). Conceptual representation of early adolescents’ prosocial behavior. Sociological Studies, (5), 169-187. |
| [35] |
Liang, Y., Zheng, H., & Liu, Z. (2020). Changes in the network of posttraumatic stress disorder among children after the Wenchuan earthquake: A four-year longitudinal study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 52(11), 1301-1312.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2020.01301 |
| [36] |
Liu, S., Zhang, D., Tian, Y., Xu, B., & Wu, X. (2023). Gender differences in symptom structure of adolescent problematic internet use: A network analysis. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health, 17(1), 49.
doi: 10.1186/s13034-023-00590-2 pmid: 37029403 |
| [37] |
Luengo Kanacri, B. P., Pastorelli, C., Eisenberg, N., Zuffianò, A., & Caprara, G. V. (2013). The development of prosociality from adolescence to early adulthood: The role of effortful control. Journal of Personality, 81(3), 302-312.
doi: 10.1111/jopy.12001 pmid: 22924862 |
| [38] |
Marchetti, I. (2019). Hopelessness: A network analysis. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 43(3), 611-619.
doi: 10.1007/s10608-018-9981-y |
| [39] | Marcus, D. K., Preszler, J., & Zeigler-Hill, V. (2018). A network of dark personality traits: What lies at the heart of darkness? Journal of Research in Personality, 73, 56-62. |
| [40] | McNally, R. J. (2016). Can network analysis transform psychopathology? Behavior Research and Therapy, 86, 95-104. |
| [41] | Mesurado, B., Guerra, P., Richaud, M. C., & Rodriguez, L. M. (2019). Effectiveness of prosocial behavior interventions:A meta-analysis. In P. Á. Gargiulo & H. L. Mesones Arroyo (Eds.), Psychiatry and neuroscience update: From translational research to a humanistic approach (Vol. 3, pp. 259-271). Springer International Publishing. |
| [42] | Opic, S. (2016). Interpersonal relations in school. International Journal of Cognitive Research in Science, Engineering and Education, 4(2), 9-21. |
| [43] | Padilla-Walker, L. M., & Carlo, G. (Eds.). (2014). Prosocial development: A multidimensional approach. Oxford University Press. |
| [44] |
Robinaugh, D. J., Millner, A. J., & McNally, R. J. (2016). Identifying highly influential nodes in the complicated grief network. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 125(6), 747-757.
doi: 10.1037/abn0000181 pmid: 27505622 |
| [45] |
Rose, A. J., & Rudolph, K. D. (2006). A review of sex differences in peer relationship processes: Potential trade-offs for the emotional and behavioral development of girls and boys. Psychological Bulletin, 132(1), 98-131.
doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.132.1.98 pmid: 16435959 |
| [46] |
Steinberg, L. (2005). Cognitive and affective development in adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(2), 69-74.
doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2004.12.005 pmid: 15668099 |
| [47] | van Borkulo, C. D., Borsboom, D., Epskamp, S., Blanken, T. F., Boschloo, L., Schoevers, R. A., & Waldorp, L. J. (2014). A new method for constructing networks from binary data. Scientific Reports, 4(1), 5918. |
| [48] | van Borkulo, C. D., Boschloo, L., Borsboom, D., Penninx, B. W. J. H., Waldorp, L. J., & Schoevers, R. A. (2015). Association of symptom network structure with the course of depression. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(12), 1219. |
| [49] |
van Borkulo, C. D., van Bork, R., Boschloo, L., Kossakowski, J. J., Tio, P., Schoevers, R. A., Borsboom, D., & Waldorp, L. J. (2022). Comparing network structures on three aspects: A permutation test. Psychological Methods, 28(6), 1273-1285.
doi: 10.1037/met0000476 pmid: 35404628 |
| [50] | van Buuren, S., & Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K. (2011). mice: Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. Journal of Statistical Software, 45(3), 1-67. |
| [51] | Wentzel, K. R. (1993). Does being good make the grade? Social behavior and academic competence in middle school. Journal of Educational Psychology, 85(2), 357-364. |
| [52] |
Wentzel, K. R., Filisetti, L., & Looney, L. (2007). Adolescent prosocial behavior: The role of self-processes and contextual cues. Child Development, 78(3), 895-910.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.01039.x pmid: 17517011 |
| [53] | Yang, Y., Kong, X., Guo, Z., & Kou, Y. (2021). Can self-compassion promote gratitude and prosocial behavior in adolescents? A 3-year longitudinal study from China. Mindfulness, 12(6), 1377-1386. |
| [54] | Yang, Y., Zhang, M., & Kou, Y. (2016). The revalidation and development of the prosocial behavior scale for adolescent. Chinese Social Psychological Review, 10, 135-150. |
| [55] | Zhang, M., Yang, Y., & Kou, Y. (2015). The adolescents’ prosocial behavior and its development. Youth Studies, (4), 10-18. |
| [56] | Zhang, Q. (2012). The dimensions of measurement and mechanism of prosocial behavior from a perspective of conceptual representation (Unpublished doctorial dissertation). Beijing Normal University. |
| [57] | Zhang, Q., & Kou, Y. (2011). The dimension of measurement on prosocial behavior: exploration and confirmation. Sociological Studies, 11, 105-121. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||